Powder fillers in powder coatings not only reduce costs but also play a great role in improving the performance of coating products. They improve coating wear resistance, scratch resistance, and reduce sagging during melting and leveling. Powder fillers also enhance corrosion resistance and improve moisture resistance.
When selecting powder fillers for powder coatings, factors like density, dispersibility, particle size distribution, and purity must be considered. Generally, higher density results in lower coverage of the powder coating. Larger particles disperse better than smaller particles. Fillers should be chemically inert to avoid reactions with certain components, such as pigments. Ideally, fillers should have a white color. Common powder materials used in coatings include calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, talc powder, mica powder, kaolin, silica, and wollastonite.

Application of Calcium Carbonate in Powder Coatings
Calcium carbonate (as powder fillers) is divided into light calcium carbonate (precipitated calcium carbonate) and heavy calcium carbonate. Regardless of the type or production method, the particle size of calcium carbonate strongly affects the coating’s gloss. Calcium carbonate is generally not recommended for outdoor use.
Heavy calcium is mainly used to increase volume, partially replace titanium dioxide and color pigments, and substitute light calcium and precipitated barium sulfate. It also helps with corrosion resistance and partially replaces anti-rust pigments.
When used in indoor architectural coatings, heavy calcium can be used alone or in combination with talc powder. Compared to talc powder, calcium carbonate reduces chalking rate, improves color retention of light-colored paints, and increases anti-mold properties. However, due to its poor acid resistance, its use in exterior coatings is limited.
Compared to heavy calcium, light calcium has smaller particle size, narrower particle size distribution, higher oil absorption, and brightness. Light calcium is ideal for applications requiring the highest degree of matting.

Application of Barium Sulfate in Powder Coatings
Barium sulfate used as a coating extender pigment comes in two forms: natural and synthetic. The natural product is known as barite powder, while the synthetic product is precipitated barium sulfate.
In powder coatings, precipitated barium sulfate enhances the leveling and gloss retention of the coating, and has good compatibility with all pigments. It helps achieve the ideal film thickness during the spraying process, with a high powder transfer rate.
Barite powder is mainly used in industrial primers, automotive intermediate coatings, and high-strength coatings that require high film strength, high filling power, and chemical inertness. It is also used in topcoats that require high gloss. In latex paints, due to its high refractive index (1.637), fine barite powder can function as a semi-transparent white pigment, replacing some titanium dioxide in the coating.
Application of Mica Powder in Powder Coatings
Mica powder is composed of complex silicate minerals with flaky particles, offering excellent heat and acid/alkali resistance. It affects the melting flowability of powder coatings and is typically used in heat-resistant and insulating powder coatings. It can also be used as a filler for texture powders.
Among the various types of mica, sericite mica has a chemical structure similar to kaolin, combining features of both mica and clay minerals. When applied in coatings, it significantly improves weather resistance, water resistance, and enhances adhesion and strength of the coating. It also improves the appearance of the coating. Dye particles easily enter the interlayer spaces of sericite mica, helping the color remain vibrant and resistant to fading. In addition, sericite mica has algae and mildew resistance properties. Therefore, sericite mica powder is a multifunctional filler with excellent cost-performance ratio for coatings.

Application of Talc Powder in Powder Coatings
Talc powder, also known as hydrous magnesium silicate, is made by directly grinding talc ore. The particles are needle-shaped crystals, offering a slippery feel, soft texture, and low abrasiveness. It has good suspension, dispersion, and some thixotropic properties, significantly affecting the melting flowability of powder coatings. Talc powder is commonly used in texture powders and is found in various primers, intermediate coatings, road marking paints, industrial coatings, and both interior and exterior architectural paints.

Application of Silica in Powder Coatings
Porous quartz, a type of silica, is widely recognized for its safety and is commonly used in powder coatings, fireproof coatings, waterproof coatings, and anti-corrosion coatings. Inexpensive porous quartz can help reduce the cost of powder coatings while replacing barium sulfate to lower the soluble barium content in the product, meeting environmental requirements.

Application of Kaolin in Powder Coatings
Kaolin can improve thixotropy and anti-settlement properties. Calcined clay does not affect rheological performance but, like untreated clay, provides matting effects, increases opacity, and boosts whiteness, similar to talc powder.

Kaolin generally has high water absorption, making it unsuitable for improving thixotropy or for producing water-repellent coatings. Kaolin products typically have a particle size range of 0.2–1μm. Larger particle size kaolin has lower water absorption and better matting effects, while smaller particle size kaolin (below 1μm) is suitable for semi-gloss coatings and interior paints.
Application of Hollow Glass Microspheres in Powder Coatings
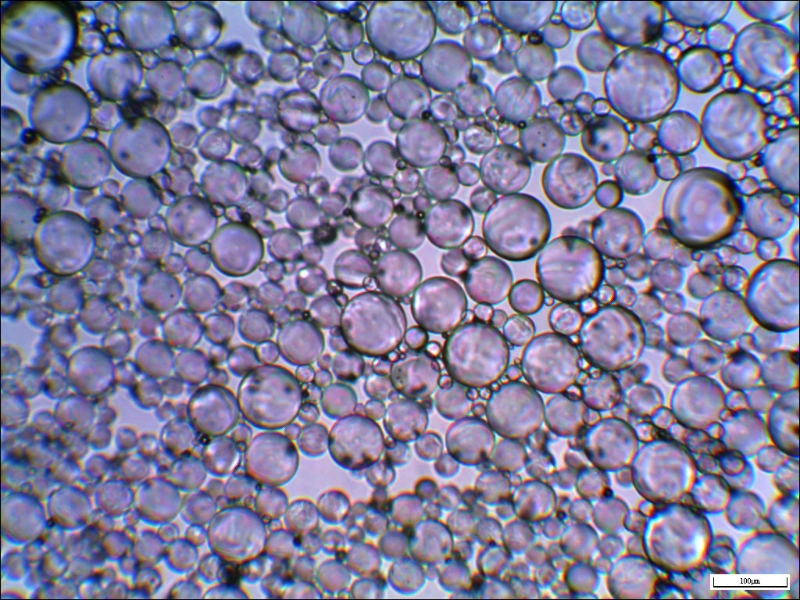
Hollow glass microspheres are small, hollow, spherical powders with advantages such as low weight, large volume, low thermal conductivity, high compressive strength, insulation, corrosion resistance, non-toxicity, and good dispersion, flowability, and stability.
When applied in powder coatings, hollow glass microspheres provide the following benefits:
Thermal Insulation, Insulation, and Low Water Absorption:
The interior of hollow glass microspheres is either a vacuum or filled with low-density gas, giving them a significant difference in density and thermal conductivity compared to epoxy resins. This makes them excellent thermal insulators and ideal fillers for high-temperature powder coatings.
Improvement of Physical and Mechanical Properties:
Hollow glass microspheres can increase the hardness and rigidity of the powder coating. However, their impact resistance decreases, with the extent of the reduction depending on the surface treatment of the microspheres. Proper pre-treatment with coupling agents can minimize the negative impact on impact resistance.
Low Oil Absorption:
Different grades of hollow glass microspheres have an oil absorption rate ranging from 7mg to 50mg per 100g. This low oil absorption allows the material to increase the filling volume during production, reducing overall costs.
Application of Wollastonite in Powder Coatings
Wollastonite mainly consists of calcium silicate, with a density of 2.9g/cm³, a refractive index of 1.63, and an oil absorption rate of 30–50%. It has a needle-like structure and good brightness.
In powder coatings, natural wollastonite powder, made from processed natural wollastonite, is commonly used. Wollastonite serves as an extender pigment in coatings and can replace a portion of white pigments, providing opacity and increasing volume, thus reducing the cost of the paint. Due to its excellent conductivity, wollastonite is often used in epoxy insulation powder coatings. Its white, needle-like structure helps improve the bending and stretching properties of powder coatings.
conclusion
Powder coatings are energy-efficient, resource-saving, and environmentally friendly coatings. As global demand for energy increases, reducing energy consumption and protecting the environment have become key development priorities. Therefore, the future direction of powder coatings development will focus on low-temperature curing, high weather resistance, strong decorative properties, and the ability to be applied in thin layers. Driven by the increasing demand for powder coatings, the need for powder fillers such as calcium carbonate, quartz, mica powder, talc, and kaolin will inevitably grow as well.
epic powder
Epic Powder, 20+ years of work experience in the ultrafine powder industry. Actively promote the future development of ultra-fine powder, focusing on crushing, grinding, classifying and modification process of ultra-fine powder. Contact us for a free consultation and customized solutions! Our expert team is dedicated to providing high-quality products and services to maximize the value of your powder processing. Epic Powder—Your Trusted Powder Processing Expert !

